Evaluation
Regret
pyepo.metric.regret evaluates the decision quality of a prediction model. Regret is defined as \(l_{Regret}(\hat{\mathbf{c}}, \mathbf{c}) = \mathbf{c}^T \mathbf{w}^*(\hat{\mathbf{c}}) - z^*(\mathbf{c})\), which measures the gap between the objective value achieved by the predicted solution and the true optimum.
- pyepo.metric.regret(predmodel, optmodel, dataloader)
A function to evaluate model performance with normalized true regret
- Parameters:
predmodel (nn) – a regression neural network for cost prediction
optmodel (optModel) – a PyEPO optimization model
dataloader (DataLoader) – Torch dataloader from optDataSet
- Returns:
true regret loss
- Return type:
float
import pyepo
regret = pyepo.metric.regret(predmodel, optmodel, testloader)
Unambiguous Regret
When a predicted cost vector \(\hat{c}\) yields multiple optimal solutions for \(\underset{\mathbf{w} \in S}{\min}\;\hat{\mathbf{c}}^T \mathbf{w}\), the unambiguous regret considers the worst case: \(l_{URegret}(\hat{\mathbf{c}}, \mathbf{c}) = \underset{\mathbf{w} \in W^*(\mathbf{c})}{\max} \mathbf{w}^T \mathbf{c} - z^*(\mathbf{c})\).
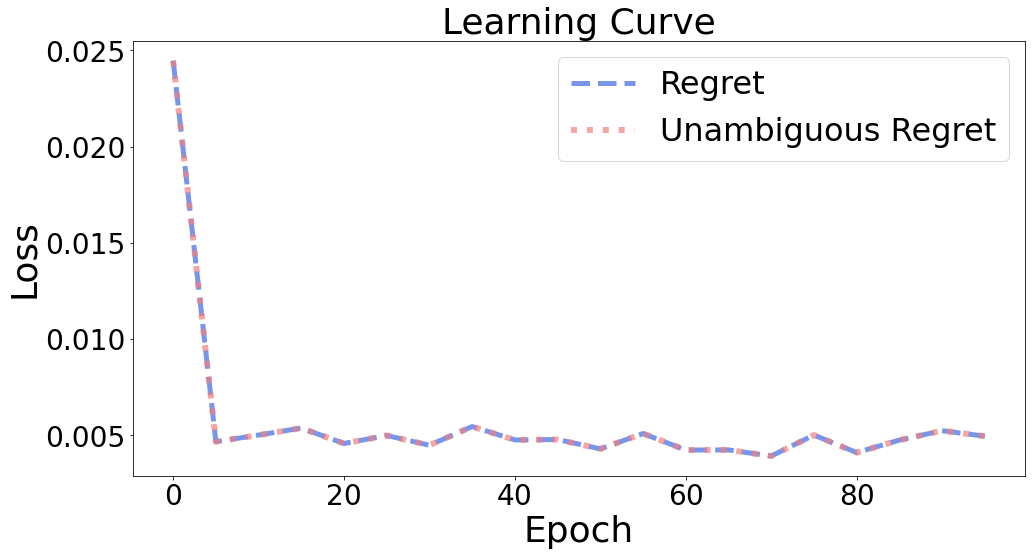
As the figure shows, regret and unambiguous regret are nearly identical across all training procedures. While the unambiguous regret is more theoretically rigorous, using it in practice is generally unnecessary.
- pyepo.metric.unambRegret(predmodel, optmodel, dataloader, tolerance=1e-05)
A function to evaluate model performance with normalized unambiguous regret
- Parameters:
predmodel (nn) – a regression neural network for cost prediction
optmodel (optModel) – a PyEPO optimization model
dataloader (DataLoader) – Torch dataloader from optDataSet
tolerance (float) – tolerance for optimization
- Returns:
unambiguous regret loss
- Return type:
float
import pyepo
regret = pyepo.metric.unambRegret(predmodel, optmodel, testloader)